Dr. Oron Frenkel, an emergency physician, ultrasound educator, and Chairman of the Clarius Medical Advisory Board, is on a mission to enable more clinicians to learn to effectively use point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS).
This year, he’s been working with our team on a series of brief instructional videos. Together, we’re thrilled to announce the launch of the new Clarius Classroom, featuring videos demonstrating how to perform ultrasound exams and diagnose common pathologies.
How to Scan the Bladder
This week, we’re showcasing an ultrasound exam that’s frequently used in health care settings to avoid costly and unnecessary procedures. It’s a quick, painless, and non-invasive exam that is widely recognized as more effective and definitive than manual palpation to measure bladder volume, diagnose pathology, and visualize debris.
The Clarius C3 HD curvilinear ultrasound scanner has an automated bladder preset for fast and easy exams.
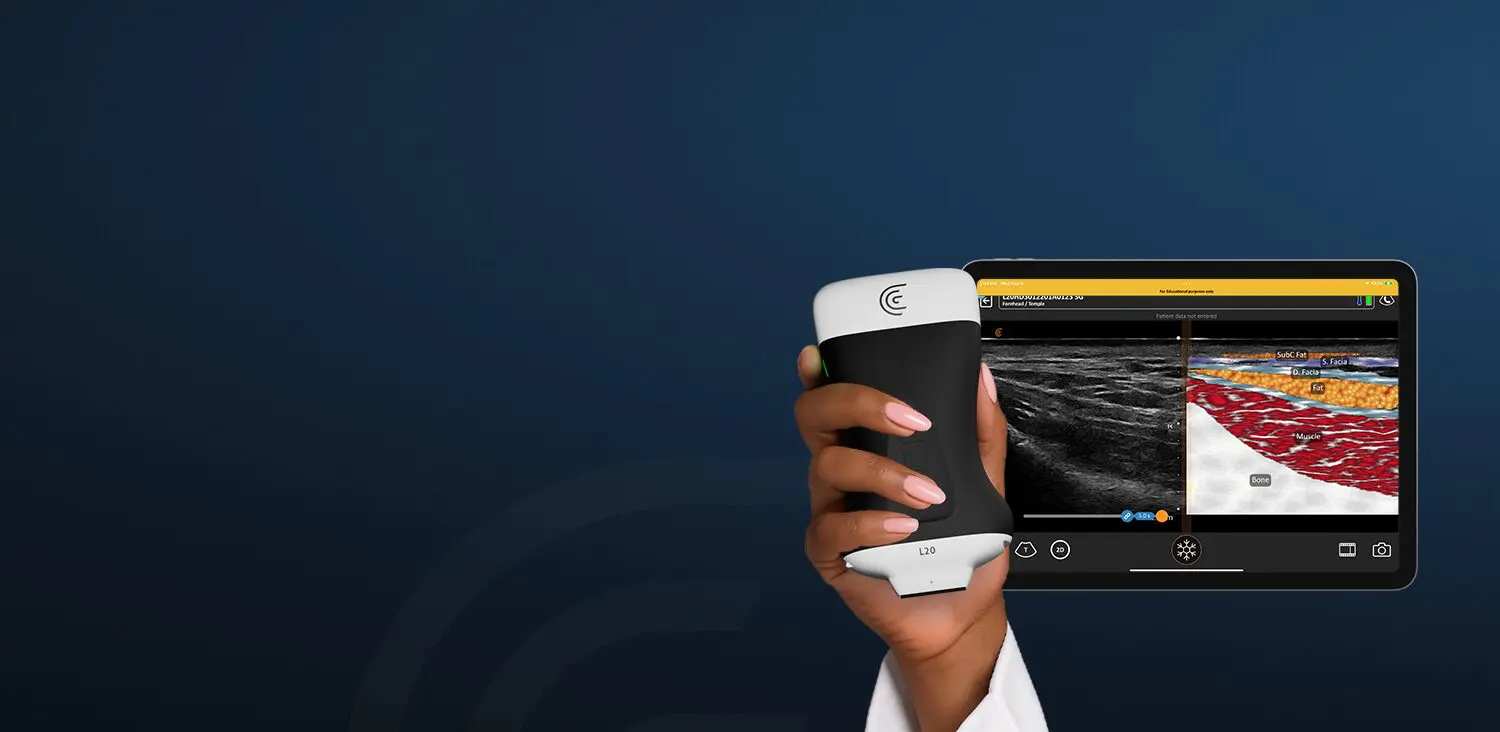
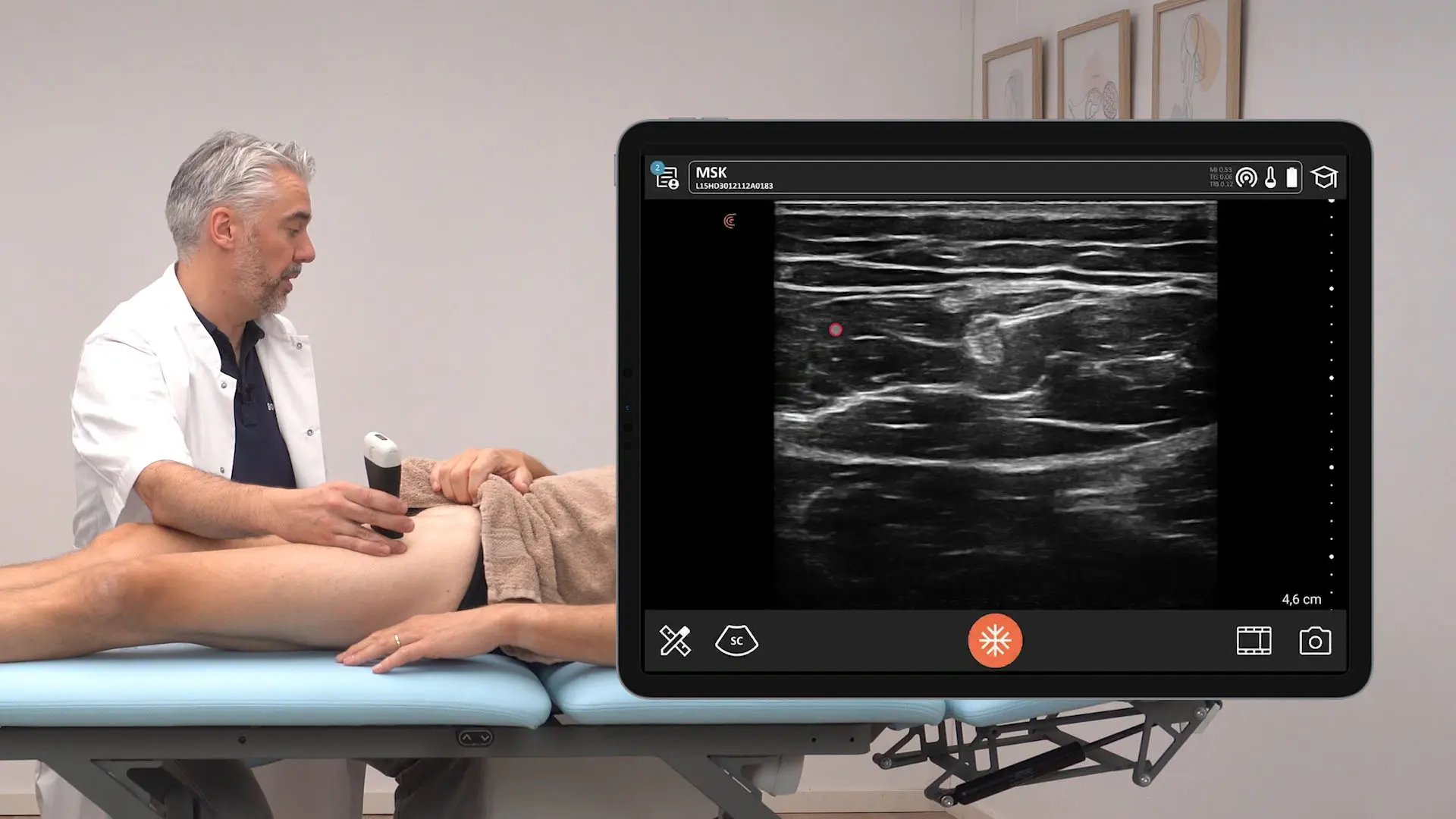
In the following two-minute Clarius Classroom video, Dr. Frenkel shows us how to perform a bladder scan to quickly identify if a patient has urinary retention or hesitancy. The scan enables quick bladder measurements to calculate pre- and post-void volume. Although Dr. Frenkel uses the Clarius C3 HD, his instruction offers useful tips that can be used with any ultrasound system.
During this demonstration, Dr. Frenkel uses the automated bladder preset on the Clarius C3 HD curvilinear scanner to perform the exam. With this setting, he acquires the bladder volume in a few easy steps, which you can follow.
- Select the pre-void (or post-void) setting depending on the status of the patient.
- Place the scanner on the right side, above the pelvis, and look for the large fluid-filled structure to appear.
- Once you see the maximum size of the bladder, freeze the image and place the calipers.
- With the cross marks in view, save the image by pressing the camera button on the Clarius App.
- Then unfreeze the image and rotate the scanner into the sagittal plane while keeping the bladder image in view.
- Freeze the image and place one more caliper to get the 3rd dimension. The Clarius App automatically calculates and displays the bladder volume.
- Click the camera to save the image and record the volume.
- Repeat steps after patient voids using the Post-Void setting to determine if the patient is suffering from urinary retention or hesitancy.
The new Clarius Classroom also features pathology videos to hone your diagnostic skills. Within the bladder, any hyperechoic structures are abnormal and can represent fresh blood, clot, mass, bladder stones, or foreign bodies. In the example below, you’ll notice a very thickened wall with dynamic debris within it, likely representing blood or fibrinous exudate within the bladder.
With high-quality imaging and an AI-driven app that is almost as easy to use as your smart phone, Clarius is the ideal ultrasound system for clinicians who are new to ultrasound. To learn more about how easy it is to learn and use the Clarius C3 HD multipurpose ultrasound scanner for point-of-care ultrasound exams, contact us today or request an ultrasound demo.
If you’re interested in watching more ultrasound educational videos, visit the new Clarius Classroom today! We invite you to subscribe to our Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram or YouTube channel for alerts on new videos.