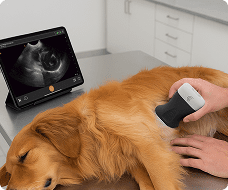
A survey scan of the elbow can identify some of the most common pathologies that cause acute and chronic elbow pain such as tendinosis of the common flexor or extensor tendons, joint effusion, or olecranon bursitis.
Clarius Classroom
Elbow
Dr. Oron Frenkel, MD
Products Used
More Classes
Request a Quote
With 8 scanners available, we offer a wireless ultrasound solution tailored to your needs. Request a quote to discover which scanner can deliver the best ultrasound imaging for your practice.
⚠️ Clarius ultrasound is for medical professionals only.
By providing my email, I consent to receive Clarius webinar invitations, case studies, whitepapers, and more, and I consent to the Clarius Privacy Policy. I can unsubscribe anytime.