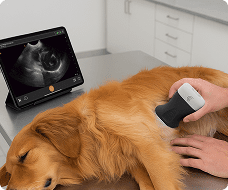
Pleural effusions can range from pure anechoic, to fibrotic (as seen here) suggesting a subacute to chronic nature, to frank iso- or hyperechoic fluid that is pathognomic for an exudate.
Clarius Classroom
Pleural Effusion
Dr. Oron Frenkel, MD
Products Used
More Classes
Request a Quote
With 8 scanners available, we offer a wireless ultrasound solution tailored to your needs. Request a quote to discover which scanner can deliver the best ultrasound imaging for your practice.
⚠️ Clarius ultrasound is for medical professionals only.
By providing my email, I consent to receive Clarius webinar invitations, case studies, whitepapers, and more, and I consent to the Clarius Privacy Policy. I can unsubscribe anytime.