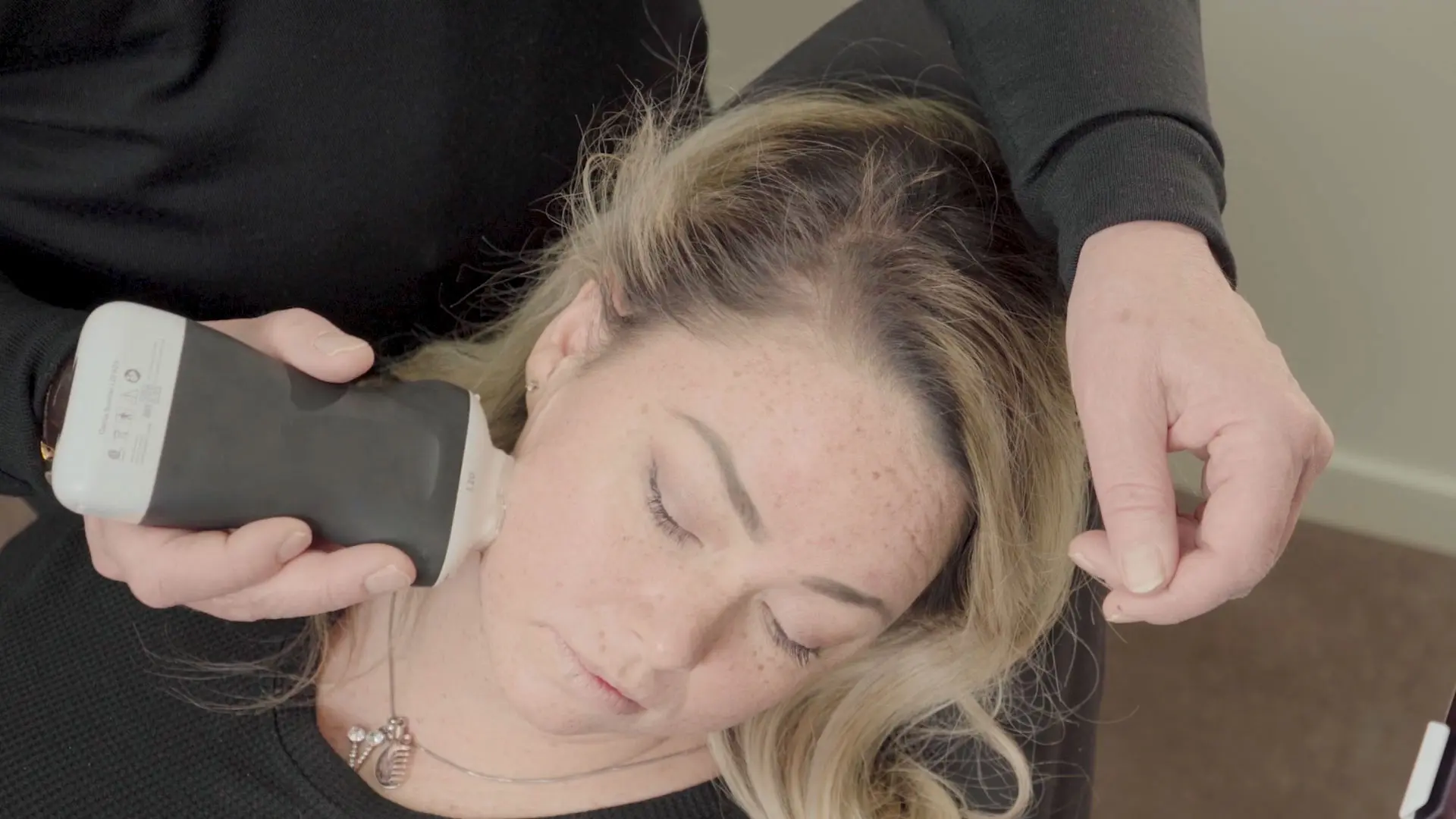
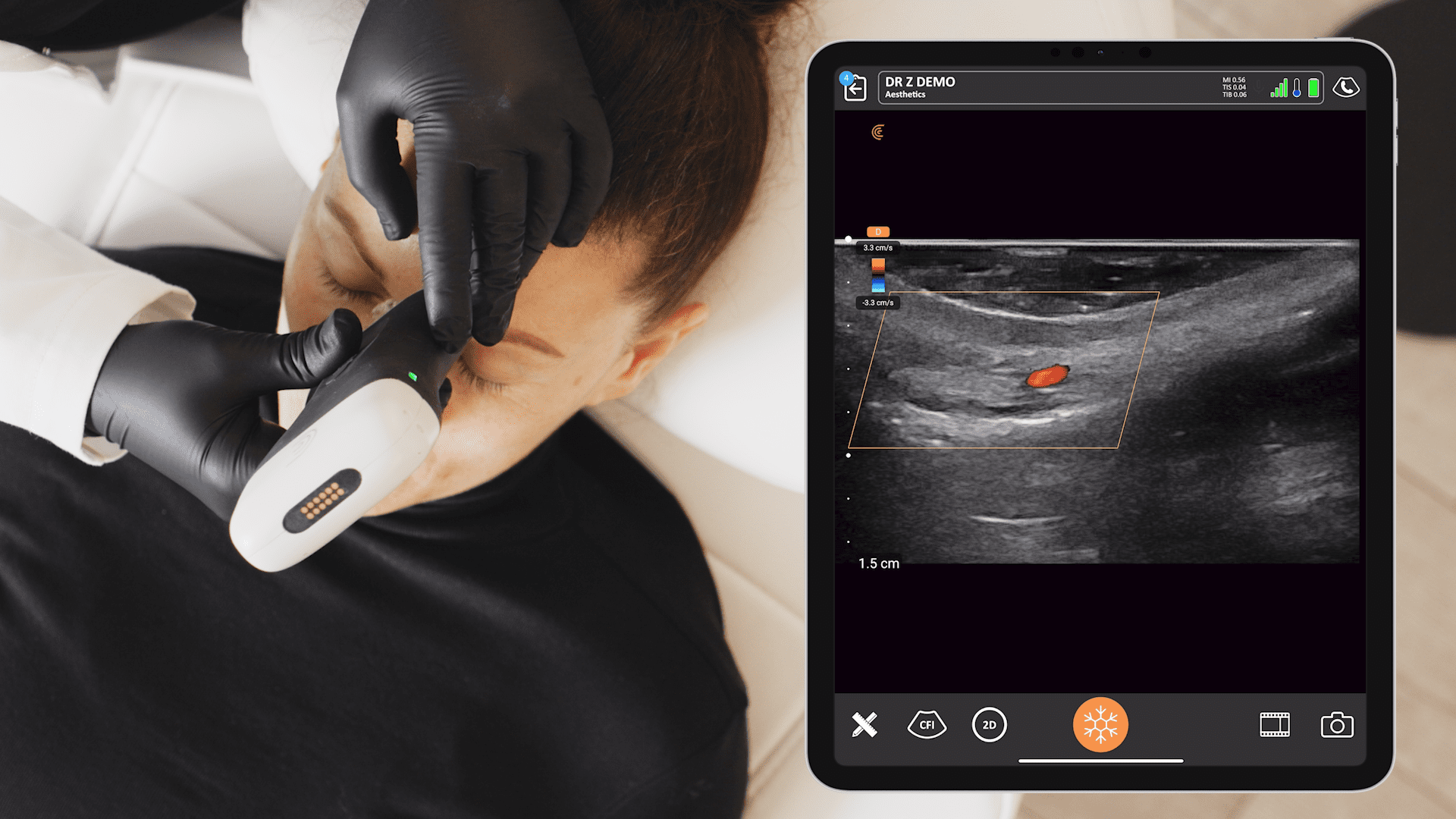
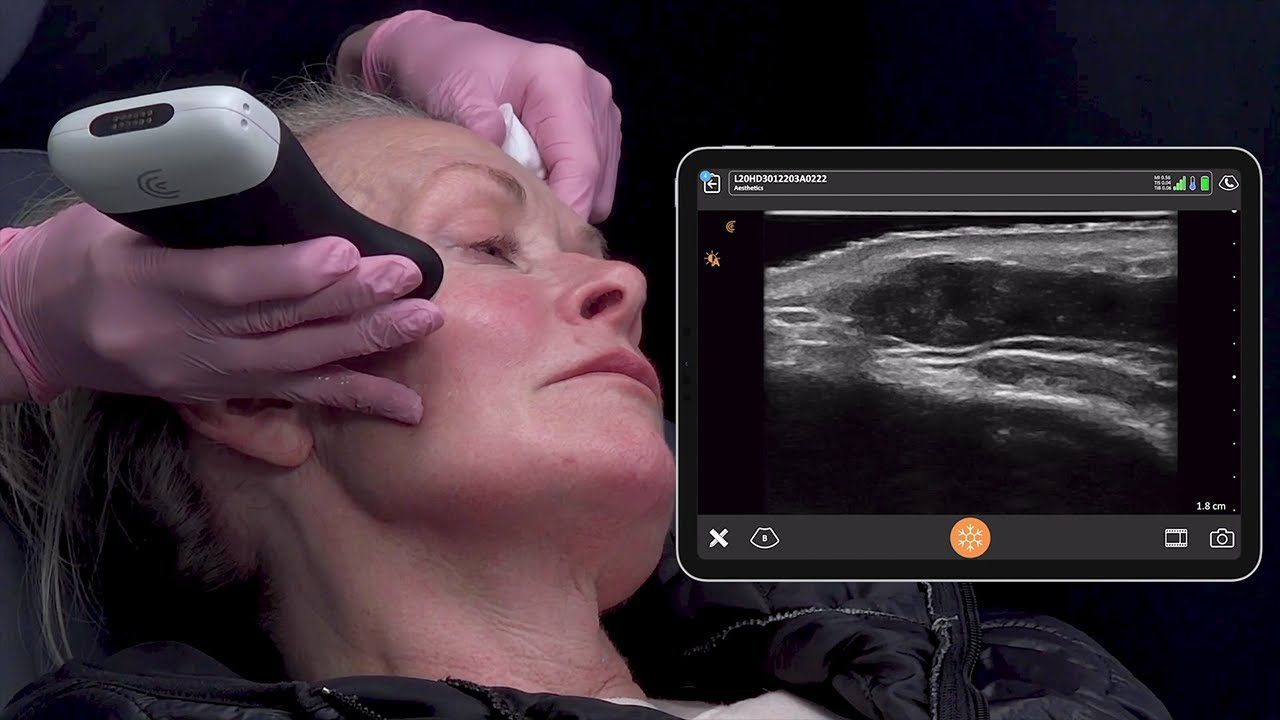
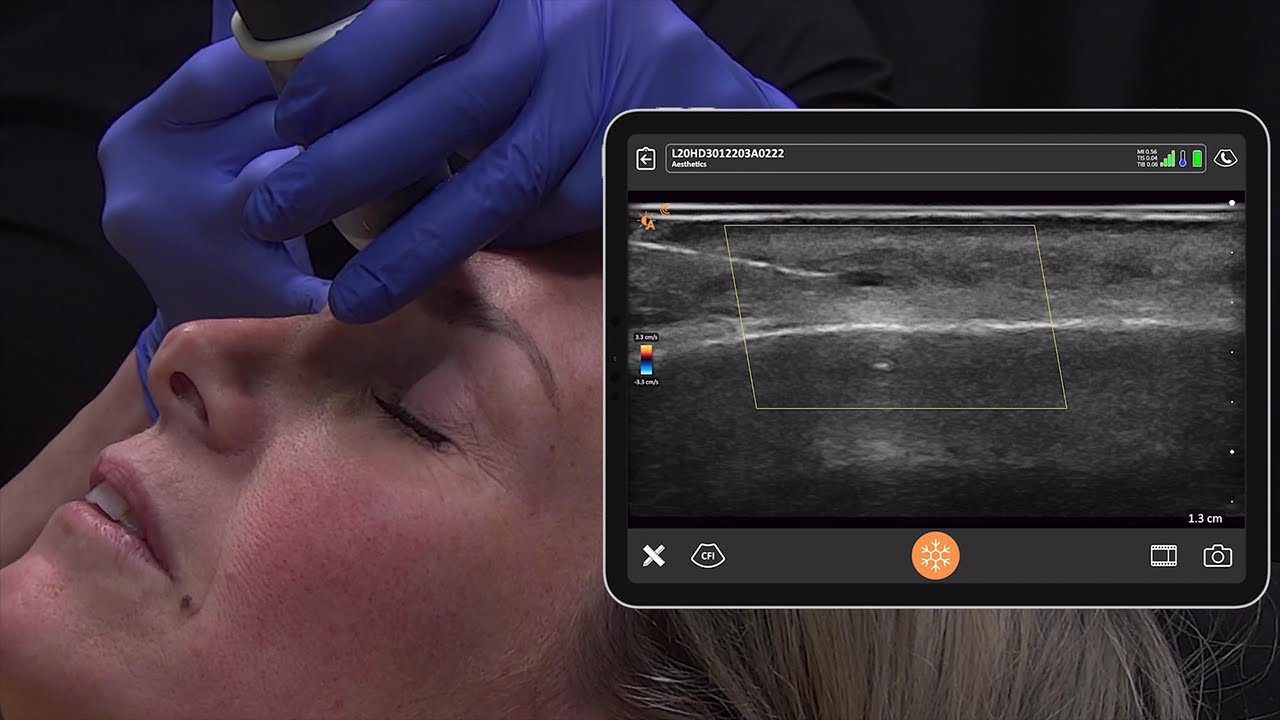
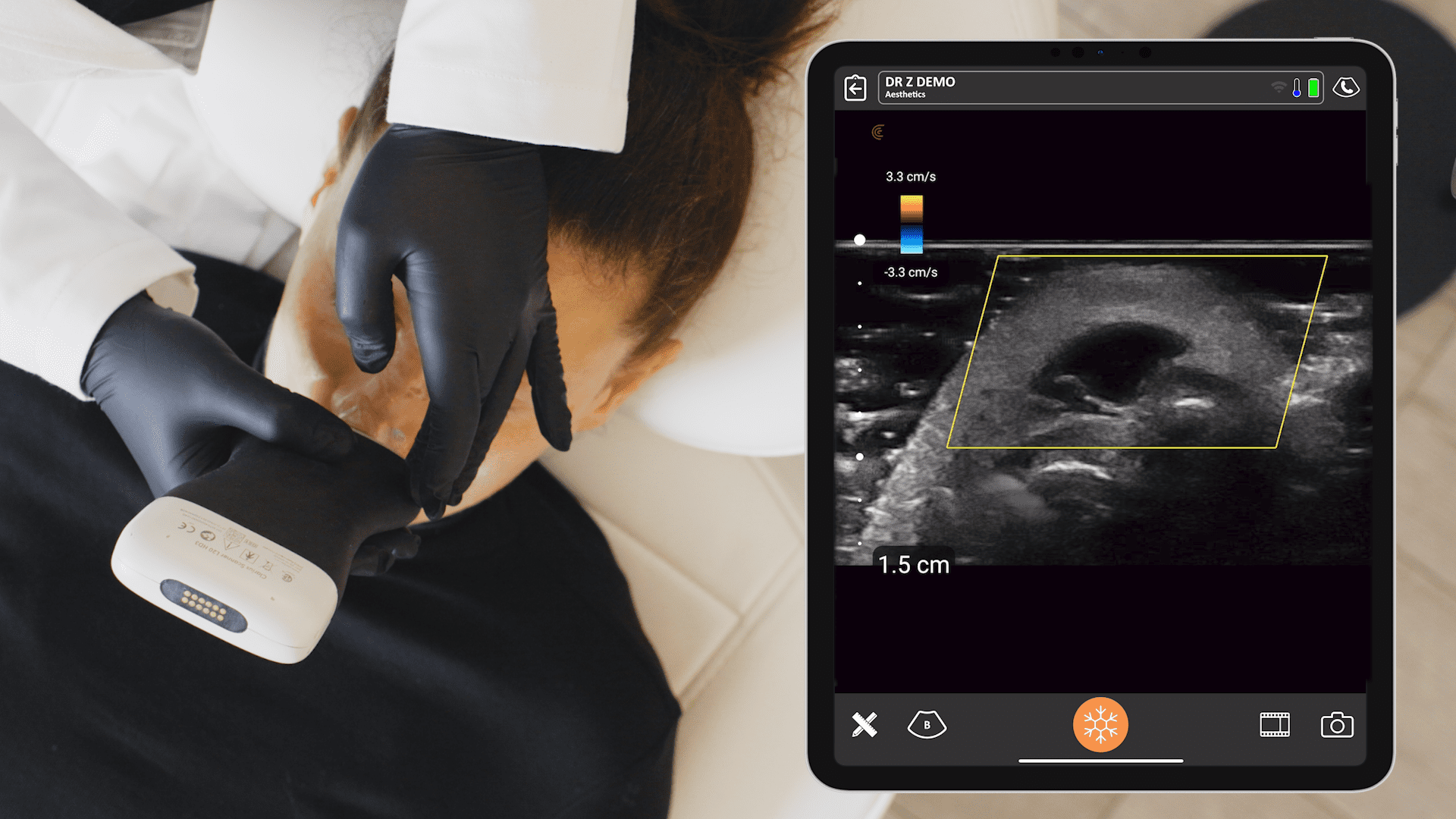
During a recent webinar, Dr. Steven F. Weiner, MD, a board-certified head, neck and facial plastic surgeon, showed us how he uses high-definition ultrasound to minimize the risks and treat complications associated with dermal filler procedures. Watch the full webinar now or read on to learn what Dr. Weiner says about how to use ultrasound to quickly evaluate fillers.
Characterizing Existing Fillers with Ultrasound
“When I see a patient who has previously had fillers, I like to identify specifically what they’ve had done for myself, because often the patient doesn’t know, particularly if the procedure took place outside the USA. Each filler has unique characteristics, which are easy to see using ultrasound.”
Hyaluronic Acid Fillers
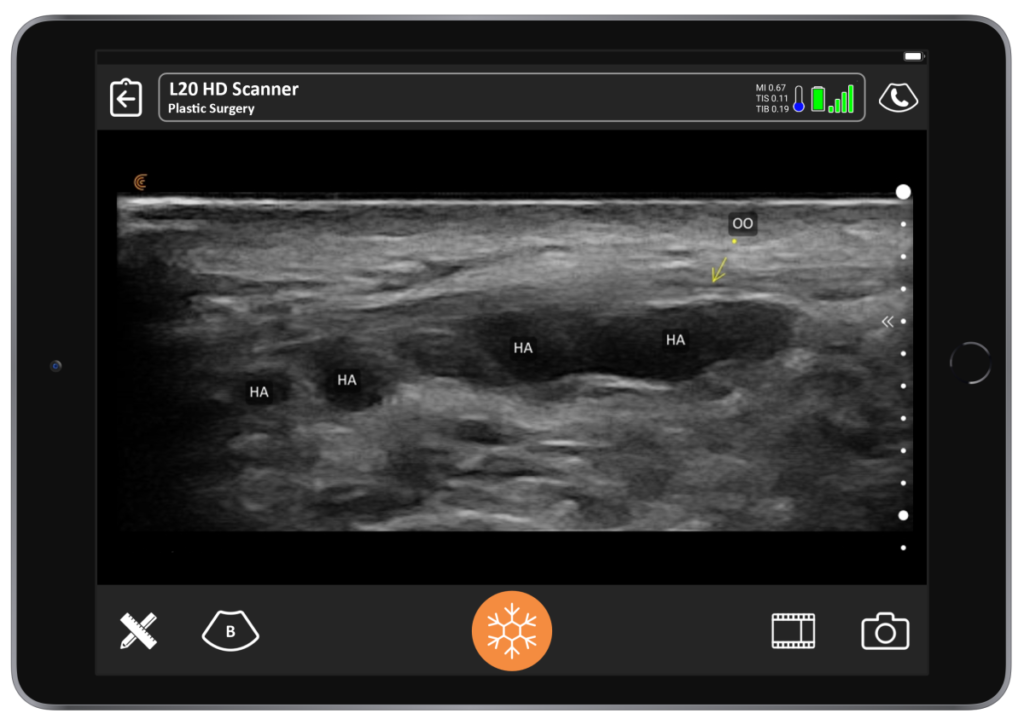
“Hyaluronic acid fillers are the most common. If it’s a recent filler, they appear as anechoic spheres on an ultrasound image because they have high water content. Sometimes they look like an oval that is angled to one side. As they lose water content over several months, they become hyperechoic – less black and grayer. You’ll see acoustic enhancement posterior to the filler, which will look white. On the following image, you see an image of a 7-year-old filler around the eye. The acoustic enhancement you see here are not true anatomic structures. These artifacts help you identify what type of filler you’re looking at.”
Calcium Hydroxyapatite (CaH)
“CaH or calcium hydroxyapatite is a hyperechoic sphere on ultrasound. That’s because it’s very difficult for the sound waves to pass through and this area reflects the ultrasound waves. On the following image captured with the Clarius L20 HD ultrasound scanner, you’ll see shadowing posterior to the hyperechoic sphere, because the sound waves aren’t going through.”
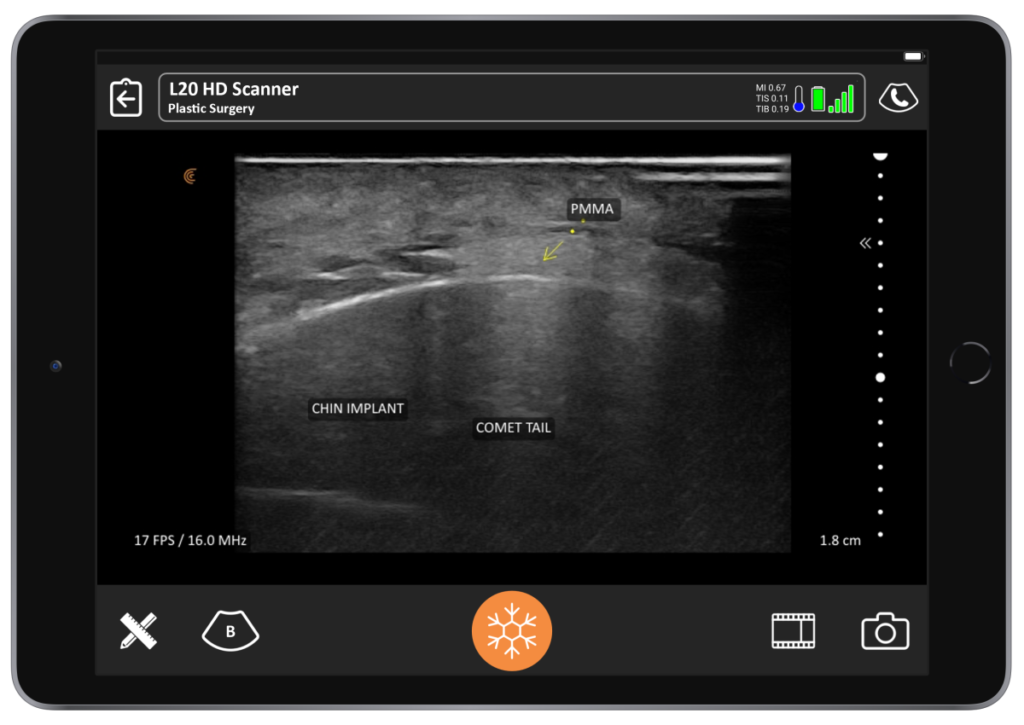
Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA)
“PMMA or polymethylmethacrylate is going to look like hyperechoic clumps with surrounding collagen on an ultrasound image. Collagen is hyperechoic. You will also have a comet-tail artifact, which is basically a V-shaped artifact that is white. You can see below that it looks like Halley’s comet. This is a chin implant. The patient needed a little more chin enhancement and opted for PMMA that was placed on the surface of the chin implant.”
Poly L Lactic Acid (PLLA)
“With PLLA or Poly L Lactic Acid, you see a diffused clouding of hyperechogenicity under ultrasound. As you know, PLLA is mostly water when you mix it. That’s why it diffuses all over the place.”
Silicone Oil
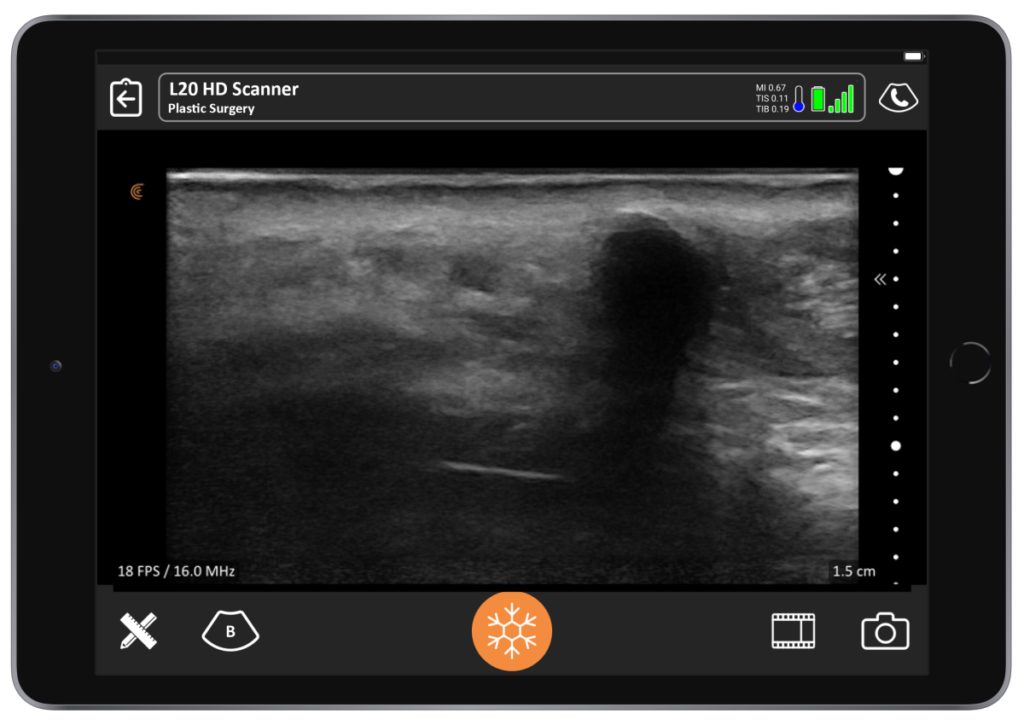
“While it’s not used much in North America, you need to know about silicone oil, because if it’s already in the patient, you do not want to inject there. Silicon appears as an ill-defined hyperechoic mass. It obscures all the anatomy below it and has a snow storm artifact on ultrasound.”
Imaging Fillers Helps Build Patient Confidence
“In the image below, you see me looking at a patient’s lip filler that was done a few weeks prior. She had the type of injection that we call tenting, fencing or the Russian technique where you go down with pillars.”
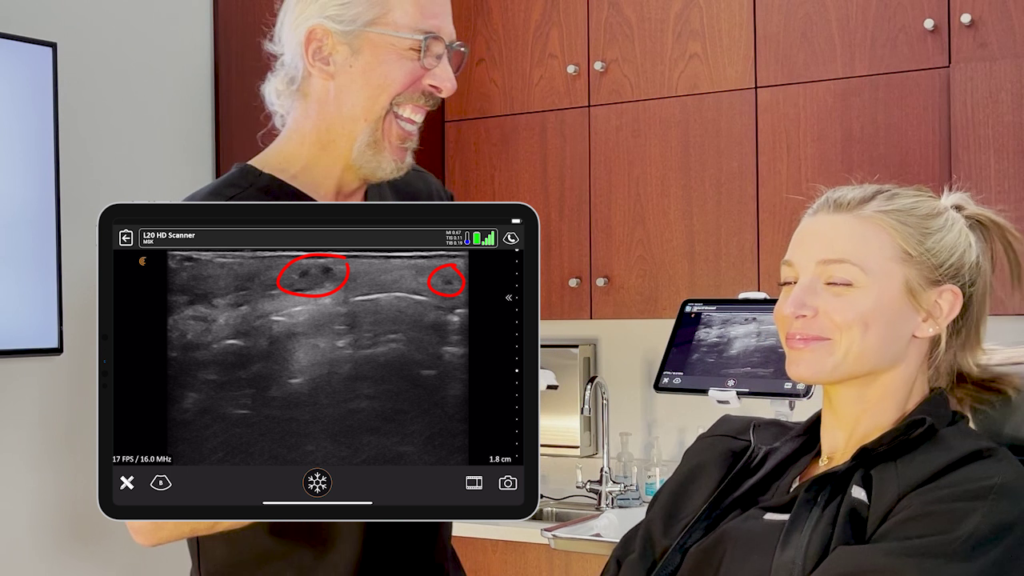
“What you see here is very small columns of HA filler that are anechoic black. And they’re placed in the exact right area, in the submucosa. I am able to show it and explain it to my patient and she’s very happy and satisfied with her results.”
Dissolving HA Fillers
“In this video you see me, as my assistant and nurse helped me to dissolve an HA filler under ultrasound guidance.”
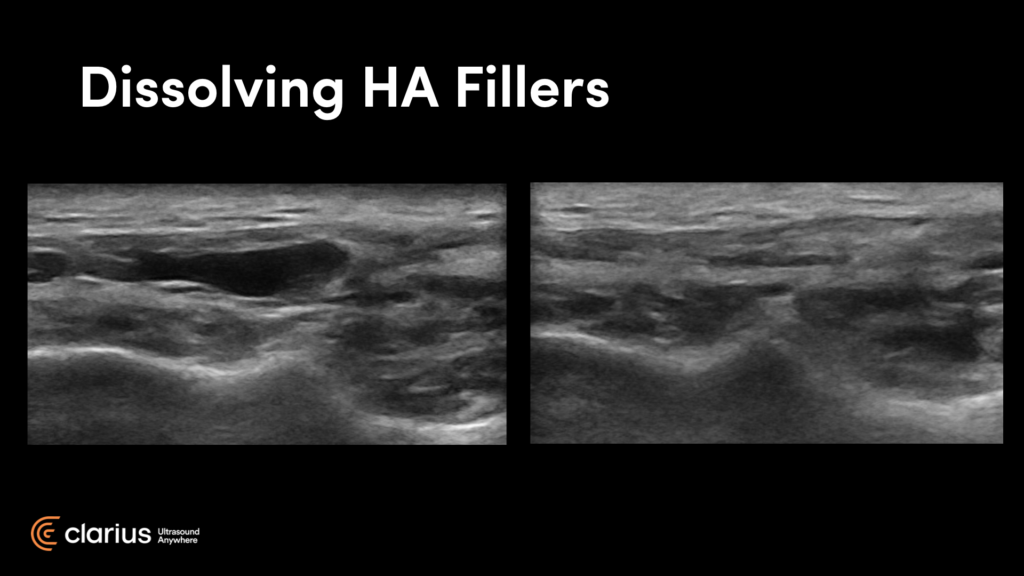
“These images you see here are of my cheek before and after. On the right is an image captured 24 hours after hyaluronic injection. You can see it’s basically dissolved. This was done under ultrasound guidance.
I had previously tried injecting this area blindly without success. You can see in the video that we are actually within the pocket. You can see the cannula right there and you can see the resolution of the nodule before your eyes. You can do this procedure by yourself on a patient with the canula in one hand and the scanner in the other, but it is a little easier with an assistant. It was a painless procedure – I just used lidocaine prior.”
Training Options
“I invite you to follow Ultrasound Facial Anatomy on Instagram, where I showcase my ultrasound techniques and imaging. My office Instagram is @aestheticclinic. You can also follow @ultrasoundfacialanatomy. My website is www.theclinique.com.”
Academy for Injection Anatomy
Dr. Steven Weiner is a faculty member of the Academy of Injection Anatomy. While courses are filling up fast, they are offering monthly training, with sessions scheduled until November 2021. A large portion is dedicated to ultrasound and anatomy, including hands-on ultrasound training using the Clarius L20 HD.
Private Training
You can also contact Dr. Weiner to book private training in small groups at his office in Santa Rosa Beach, Florida. Since Clarius is so portable, Dr. Weiner is also available to offer onsite training to groups of 8-12 people.
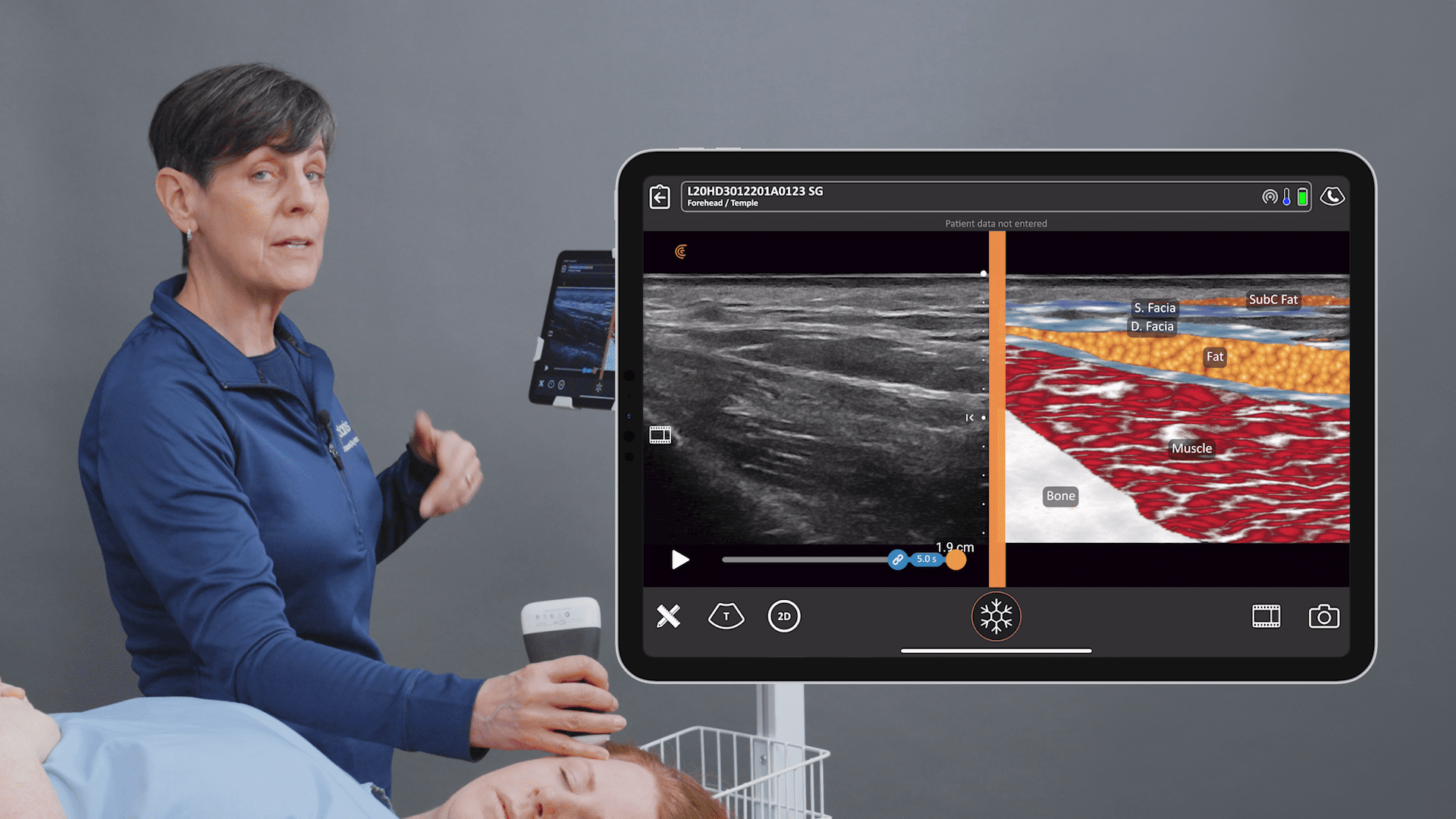
Discover the Advantages of the New Clarius L20 HD for Facial Aesthetics
Miniaturization and innovation with handheld ultrasound units means high-definition imaging is now easy and affordable, offering savings up to 80% on the cost of a traditional ultrasound system. The new Clarius L20 HD is the world’s first ultra-high frequency ultrasound in a handheld scanner, delivering ultra-high-definition imaging of the skin, muscles, vessels, and fascia for facial aesthetics.
To learn more about the ultrasound system used by Dr. Weiner, contact us today or request an ultrasound demo. We’d love to show you the difference ultra-high-definition imaging makes for facial aesthetics!