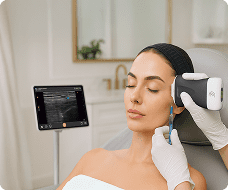
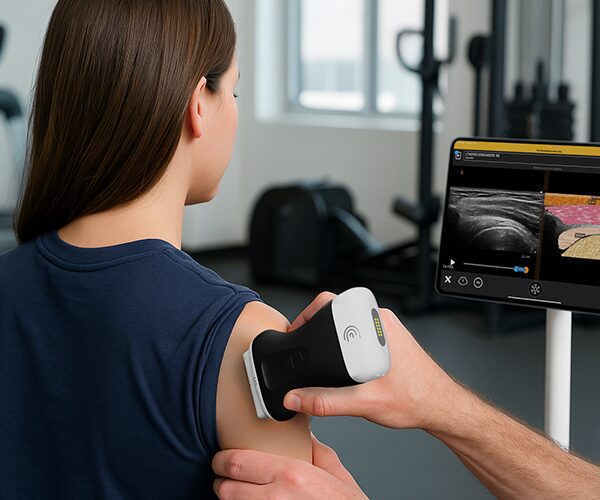
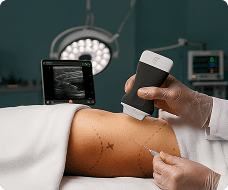
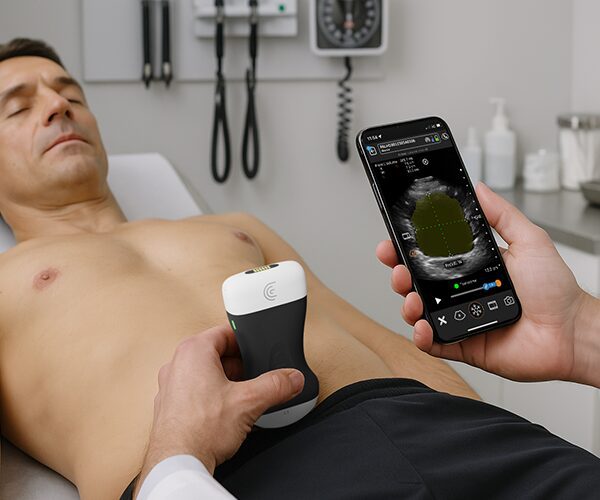
in the next video I'm going to show you how to scan the ventral shoulder in One Sweep and we're going to activate the patient so that you can also see the Zone Anatomy dynamically so we're going to place the transducer in short axis plane over the inter-tubular groove like this we're going to tilt in order to make the tendon hyperechoic I'm going to follow the long head of the biceps to distal and we're going to observe for fluid accumulation around the tendon and also for capsular changes due to his tenosynovitis at this level you can see pectoralis major tendon in Long axis plane but the short axis long end of the biceps and this is a point where the biceps is stabilized by two structures which is the pectahallis major and also the latissimus dorsi well the pectahalus major has been pointed out it's in the middle of the screen hyperechoic and now if I externally rotate the arm you can see also deep to the Bone coming from the depth a structure which is the latissimus dorsi and both latissimus and pectoralis is stabilizing the long head of the biceps and this insertion we can monitor by looking at the external rotation we're going to follow the biceps tendon down to distal and at this point what we can see is the junction towards the muscle bellies and now the muscle Bellies can be seen beautifully and what I always do is when looking at the biceps muscles especially if a long head of the biceps complete tears suspected I'm going to ask for a contraction of the muscle to see how the muscle volume behaves and also what the echogenicity of the muscle is following the biceps back towards proximal at this level what we're going to do is look at the Rotator interval and there we're going to follow the biceps and assess the relationship with the Coco humeral ligaments and also the superior cleaner humeral ligament also both stabilizing the biceps tendon in the Rotator interval so I'm going to turn the model a little bit and what I will do is I'm going to extend the arm and with this extension I'm going to internally and externally rotate the patient's arm and what we want to see is that the biceps follows the movement of the umal head and this is what's happening so this is healthy in a unstable situation you will see that the biceps will move in the opposite direction okay so turning the patient back let's follow the biceps back to the enter tubular Groove and now I'm going to look for stability in the intertubercal groove by making an in an external rotation and now we can see that the biceps is within the groove and is not luxating or dislocating during this external rotation internal rotation movement so this is also a healthy sign then from here on we're going to follow the um the the search capillar standing first and 45 degrees of external rotation I'm going to look at the insertion to the Lesser tubercle so this insertion looks fully okay and if I'm happy with the insertion then I'm going to externally rotate the arm towards 90 degrees of external rotation and then I'm going to look at the full tendon from proximal following it to a distal in order to see not only the tendon quality but also the the quality of the bone the cortical bone and also the overlying cervochromial sub deltoid bursa this I will do in Long axis plane for the subscapularis that's this one but also ensure an access plane like this and I'm going to make sure that I will see every bit of the subscapularis as it is a very large structure I'm going to scan from medial to lateral in order to see all tendon fibers in the end inserting to the Lesser tubercle last thing I want to show with the subscapularis is following back in longitudinal axis longitudinal plane the subscapularis to the coracoid process and at that level we are going to search for a subcore coil impingement so we're going to back for internal external rotation and now we're going to look for fluid collections that might pop pop up from underneath the coracoid process and we're going to search for impingement of subscapularis and Bursa at the level of the coracoid so I'm not only going to look at this level from the bone but also a little bit lower where we can see now the interaction between subscribers and Coco brachial muscle right here foreign