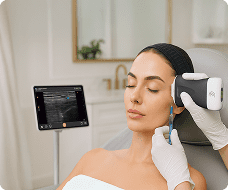
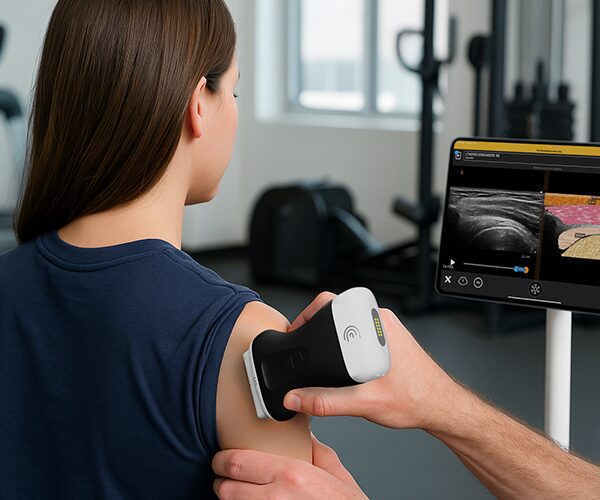
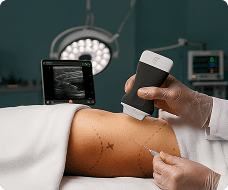
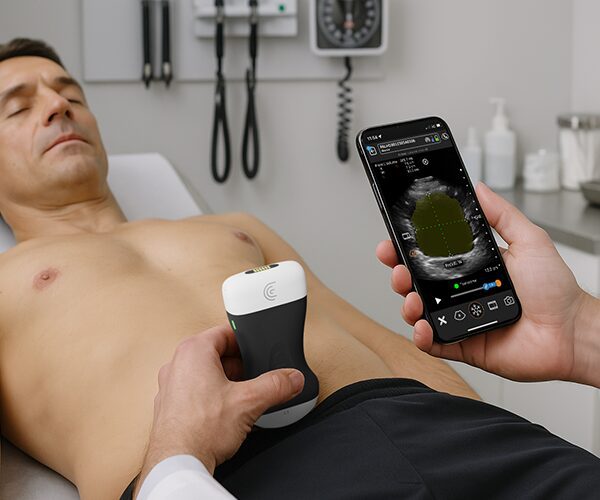
To scan the hip joint, we're going to place the patient in this supine position and then we're going to place the transducer uh longitudinal over the hip joint. Um so the uh alignment is with the uh femoral neck uh that is uh and this angle between femal shaft and femural neck is roughly about 126°. um seeking for uh the hip joint. Then uh we can see the uh acetabulum right here. Uh here we can see the uh femeral head and then this is the femoral neck. So let us modify the image uh a little bit more so that we can see it a little bit better. Yes. Uh like this. Then um here we can see the acetabulum uh also with uh the labreum the hip labreum. right there. Uh this is a part of the ilopemeral uh ligament uh the joint capsule and this ligament is running towards the femoral neck right here. And to visualize this neck we need to heel toe to distal a little bit uh so that uh the neck is more in uh in screen and more visible. So what we are going to observe is for any bony changes uh of the cortical uh bone right here uh we're going to observe uh how concave this area right there is um because there could be osteophyes there could be bony irregularities but also signs of femoral acetabular impinchment uh that there is a severity of the human head and that uh this concavity is less and Then if we uh go down to over the the femoral neck then uh we will see underneath the uh the hip joint capsule that the also part the ilio femural ligament maybe a fluid a anooic fluid which indicate a ceninoitis or maybe osteoarthritis right there. So to uh grade this fluid we're going to look at the capsule. So is the capsule is it more uh concave so following the bone than um uh it's it's it's normal. It's grade uh zero. If the capsule is straight with a h anooicic zone underneath is a grade one. Is the line a little bit higher? So more fluid underneath that's a grade two. And is there a convexity of the capsule? That would be a grade threeitis. So looking for fluids um and uh bony irregularity uh of the transition zone uh of female head to to neck and of course also in the acetabula region. Uh we can see uh the uh the labreum. uh this is not always very easy to uh to detect pathologies with the hip labum unless that there is a laboral cyst because then we see a very clear anacoic zone in the uh in the uh hip labum. Of course, what we can also do is ask the patient to um to uh or to work with the patient to make a rotation to see any kinematics uh in the hip joint. And sometimes this also influences uh uh fluid collections and also the uh the hip labum. So that is definitely something I would do as well. Static and also dynamic imaging.