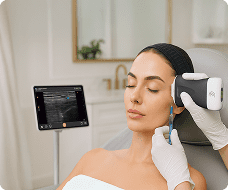
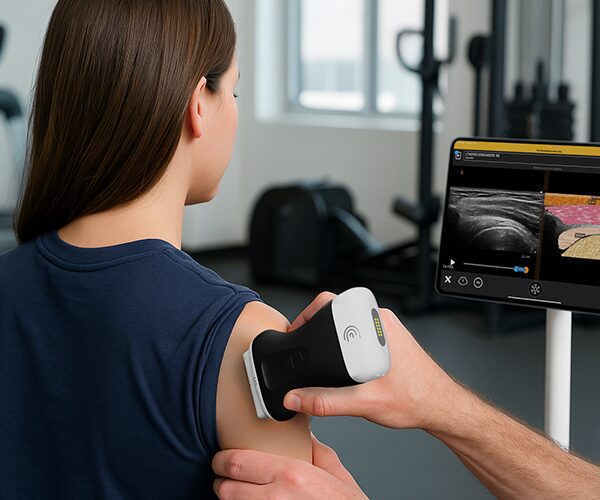
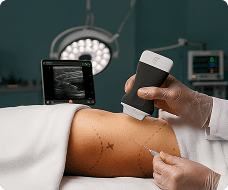
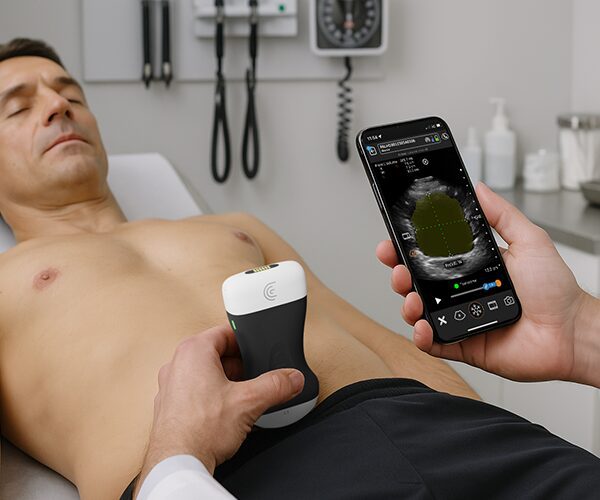
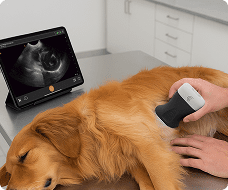
Hi, my name is Adrien Sim and I am a physiootherapist practicing pelvic health. And today I'm going to be walking you through the transabdominal approach to looking at the pelvic floor. So we're going to start with a transverse approach. So we're first going to get our client into a cric position with their knees bent and then also making sure with a transabdominal approach to looking at the pelvic floor that we ensure that the patient has a moderate amount of fluid in their bladder. So asking the patient to get one to two cups of fluid and not void before their appointment is important for the imaging piece. So we're going to come into view here. We're going to make sure that the marker of the probe is towards the patient's left which matches the screen. And then we're trying to angle the probe down in that supra pubic region. Finding the best view of the bladder. So the image should be nice and crisp in all four sides of the bladder. And then we're just starting out making an observation about the symmetry of the bladder base. So whether or not the left and right side are um looking symmetrical or whether or not there's some asymmetry and one side is looking higher than the other. Then we're going to get the client to do a pelvic floor contraction and a relaxation. And we're going to do that again and then letting that go. So, we're just observing the quality of the contraction. So, a normal response to a pelvic floor contraction should be a elevation of that bladder base. And we're also looking at I'll get you to do that again. That lifting of the bladder base and whether or not it's symmetrical or again there's some asymmetry and just making a comment of that. And then we're also looking at the quality of the relaxation. So, is it complete? Is it partial? Or is it not relaxing at all? So, I'll get you to do one more. So, we're seeing that bladder base lift. And in this case, we're seeing a little bit more of the left side elevate more than the right. Um, but we're getting a nice complete relaxation down. And I'll get you to do one more time there. And then letting it go. Good. From there, I'm going to orient the probe to the sagittal plane. So, I'm going to take the marker up towards the client's head and then angle the probe down even further here. So, in this position here, we have the urethra off to the right side of the screen and then I'm going to get the client again to contract their pelvic floor and then letting that go. So, again, observing the contraction, which should be again a view of elevation of that bladder base and then letting go and descending back down. And that wraps up the transverse and sagittal views for transabdominal pelvic floor assessment.