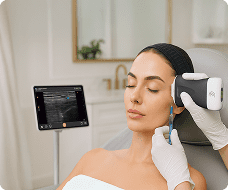
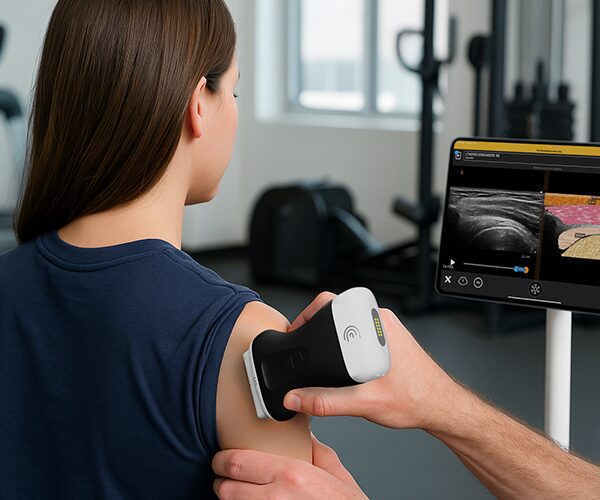
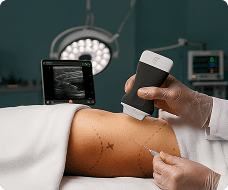
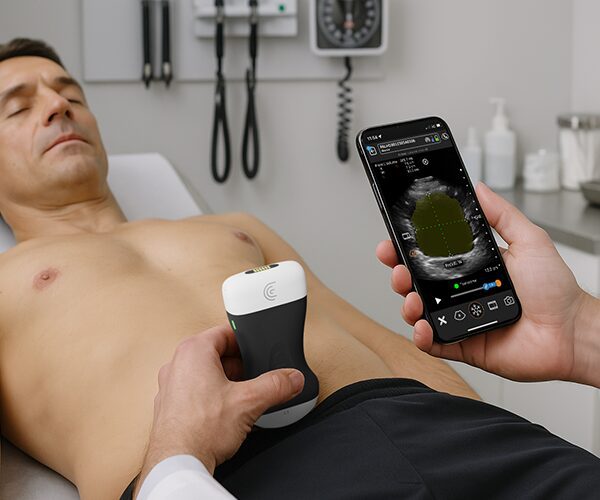
hello I'm Brian Johnson I'm an Emergency Physician and today we're going to use the clarus pal ultrasound probe to identify the subclavian landmarks for a subclavian central line typically we don't do many subclavian lines we do internal jugular Central lines and femal lines but it's good to have in your armamentarium how to perform a subclavian central line and with ultrasound it improves your accuracy and minimizes your complications and so we'll demonstrate where to approach the subclavian both in the infraclavicular and the super clavicular approach I'll demonstrate both of them so typically you have it in Venus setting which is a good setting on the Claris pal and the patient suine and typically we're going to do the right sub claven if we can so for the first one the infraclavicular approach we're going to kind of put the probe typically near the sternal notch and just below the clavicle and identify landmarks you'll see rib and lung sliding slowly move lateral and and rock the probe back and forth until you identify the pertinent structures most notably the subclavian vein typically the subclavian artery is deeper and what you want to do is identify where the subclavian vein joins with the axillary vein and that's what you culate for central line now this should be performed in the long axis so rotating your probe 90° and rocking back and forth until you identify the subclavian vein in Long axis such as this you'll see below it is the subclavian artery and the subclavian vein is what you see on view right now you would sterilize and cannulate as you would do a normal central line so that's the INF clavicular approach the super clavicular approach is where you're getting into the subclavian above o the clavicle now the internal jugular vein actually joins with the subclavian vein and that's where you actually going to do your super cicular subclavian approach what I do is typically place the probe over the right side of the neck and what I do is I identify the internal jugular vein which is sometimes triangular say a little more anterior lateral from the kateed and is easily compressible like so and what I do as I follow I follow that internal jugular down down down down you'll see the subclavian artery below it see how pulsatile it is and longitudinal View and above it is the internal jugular once again the internal jugular joins with the subclavian as so do you see that internal jugular subclavian vein and this is where you're going to culate for your central line You'll Go once again in long AIS approach using sterile precautions and standard seldinger technique so using ultrasound you can perform a so clavian central line with better accuracy and minimize your complications thank you