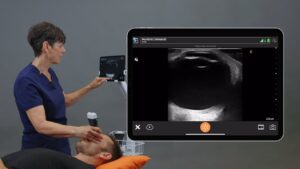
As Dr. Tom Cook illustrated during a recent webinar with 2400 registrants who were not cardiac specialists, ultrasound is no longer just for cardiologists. Chest pain is one of the most common emergency department complaints and there’s typically a wide differential diagnosis list including ischemic heart disease. Watch the recording of this free webinar to learn cardiac POCUS techniques for evaluating left ventricular function and wall motion abnormalities. Scroll below for some quick highlights of what you’ll see.
Key Takeaways from Dr. Tom Cook’s Webinar: Cardiac POCUS: Coronary Artery Disease for the Non-Cardiologist
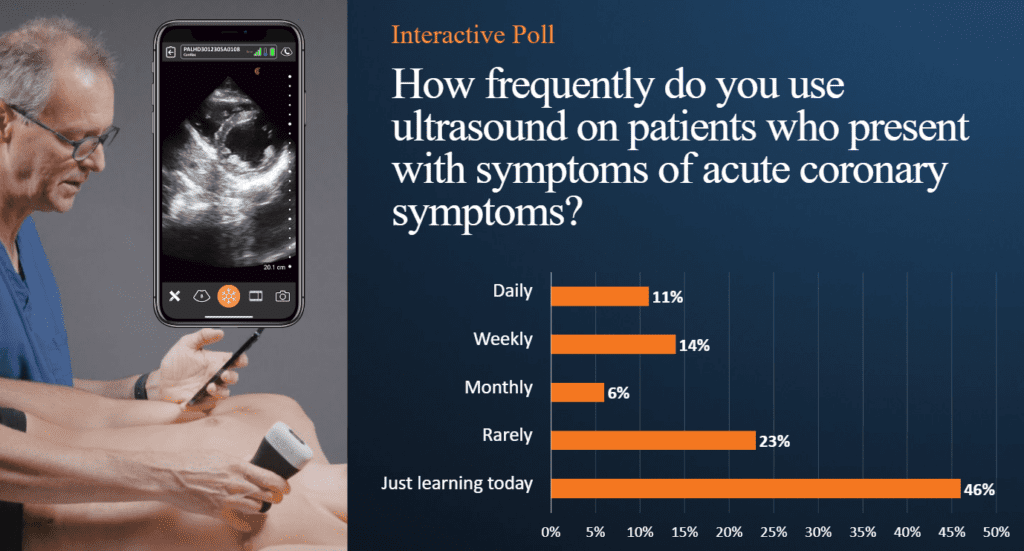
Cardiac POCUS is a powerful tool that can be used by every physician to enhance diagnostic acumen and improve patient outcomes. A quick poll of webinar attendees revealed that many physicians who aren’t using POCUS for cardiac exams, are eager to learn.
Why Cardiac POCUS Matters
- Chest Pain’s Wide Differential: Chest pain is a common ED complaint with a vast differential, including life-threatening conditions like acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
- ECG Limitations: ECGs can miss ACS, especially in non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), leading to delayed diagnosis and increased morbidity.
- POCUS as a Game-Changer: Cardiac POCUS can visualize wall motion abnormalities within seconds of myocardial ischemia, enabling rapid triage and intervention.
POCUS for Coronary Artery Disease: Key Benefits
- Early Detection: Identify wall motion abnormalities suggestive of ischemia, even in patients with atypical presentations or normal ECGs.
- Risk Stratification: Assess left ventricular function and ejection fraction to gauge the severity of CAD and guide management decisions.
- Procedural Guidance: Assist in pericardiocentesis for pericardial effusions and assess right ventricular strain in suspected pulmonary embolism.
Mastering the Views
- Apical Views:
- 4-Chamber: Visualize all four chambers and assess global left ventricular function.
- 2-Chamber: Evaluate the anterior and inferior walls.
- 3-Chamber: Assess the inferolateral wall and left ventricular outflow tract.
- Parasternal Views:
- Long Axis: Visualize the anterior and inferior walls, mitral valve, and left ventricular outflow tract.
- Short Axis: Assess all left ventricular walls and identify regional wall motion abnormalities.
A Review of Real-World Applications
Dr. Cook reviewed the following real cases during the webinar, showing healthy and pathological images and clips to help participants recognize what to look for during cardiac POCUS exams. Watch the webinar to learn his techniques.
- Young MI: A 21-year-old with atypical symptoms (vomiting) and normal vital signs had an anterior wall motion abnormality on POCUS, leading to the diagnosis of an LAD occlusion.
- Dizziness and Old MI: An elderly patient with dizziness and a normal ECG had an inferior wall motion abnormality on POCUS, revealing a previous MI and significant CAD.
- Palpitations and Dilated Cardiomyopathy: A middle-aged woman with palpitations and a normal troponin had a dilated left ventricle with apical akinesis on POCUS, indicating a prior MI and risk for arrhythmias.
- Seizure and Posterior MI: A young man with a seizure and subtle ECG changes had a posterior wall motion abnormality on POCUS, prompting immediate cath lab activation and stenting for a posterior descending artery occlusion.
- Fatigue and Takotsubo: A woman with fatigue and diffuse ST-T wave abnormalities had a dilated left ventricle with global hypokinesis on POCUS, leading to the diagnosis of Takotsubo cardiomyopathy.
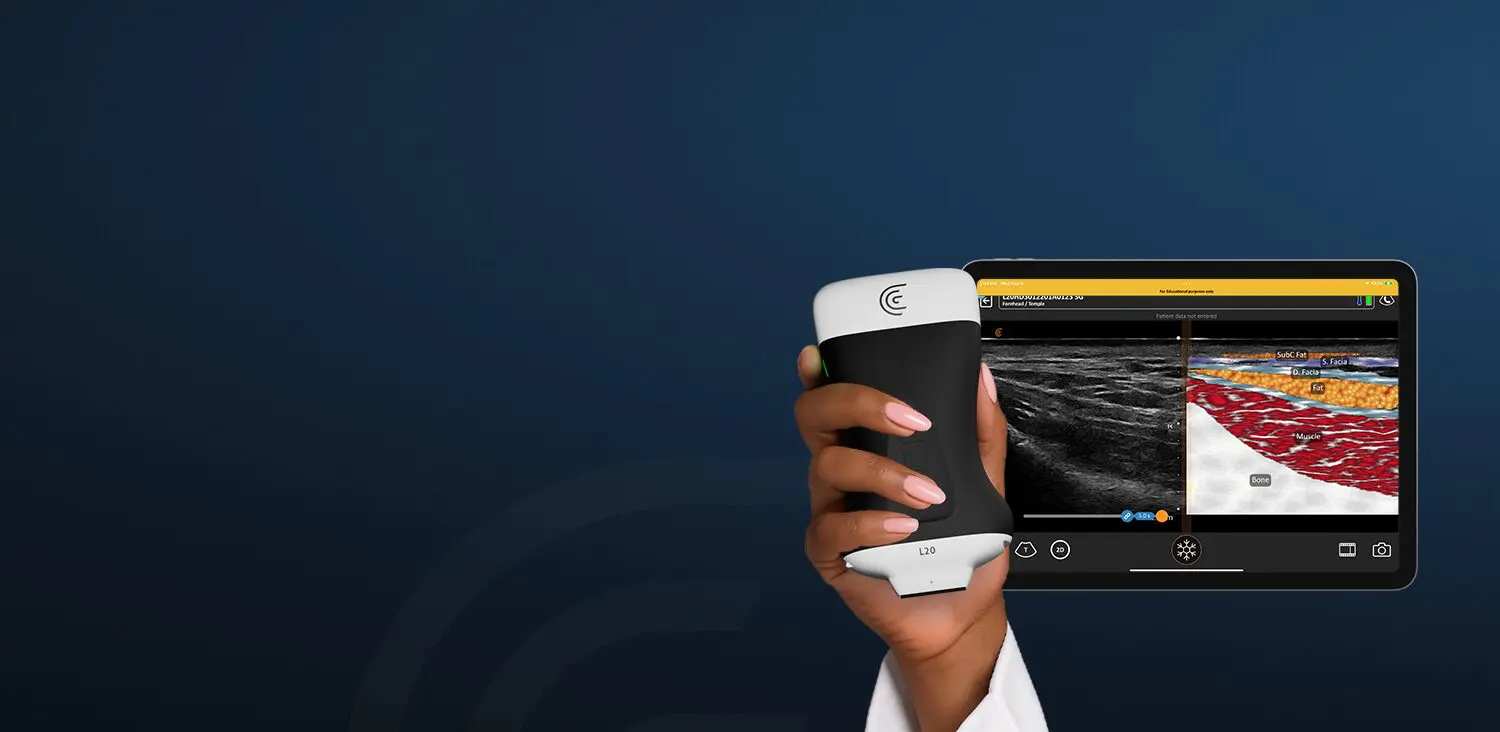
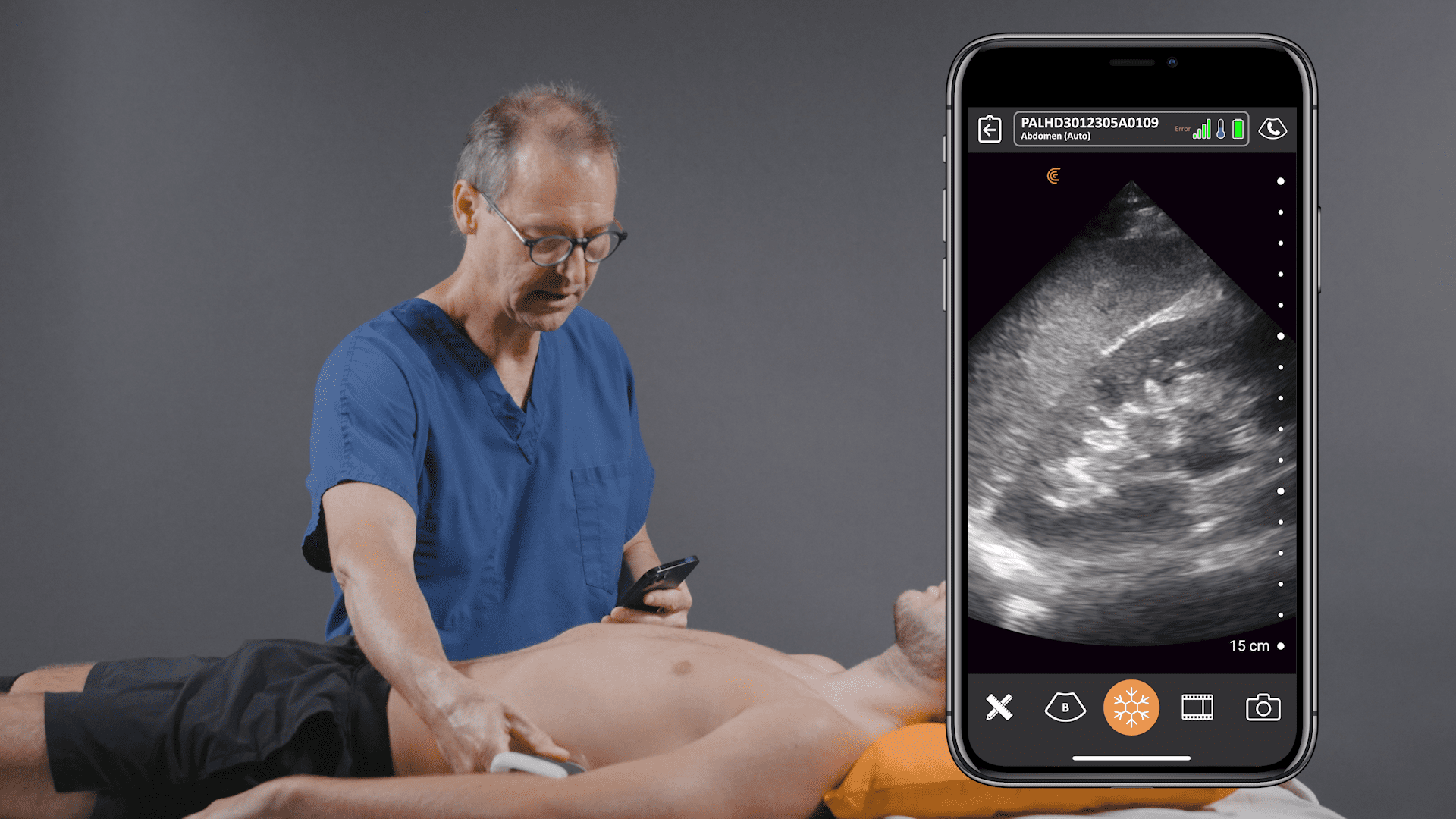
VIDEO: A Quick Assessment of Left Ventricle Function
Watch this 2-minute video to see Dr. Tom Cook demonstrate how you can quickly assess how well your patient’s heart functions from the bedside. Dr. Cook uses the Clarius PA HD3 in this video.
AI-Powered for Optimal Cardiac Imaging
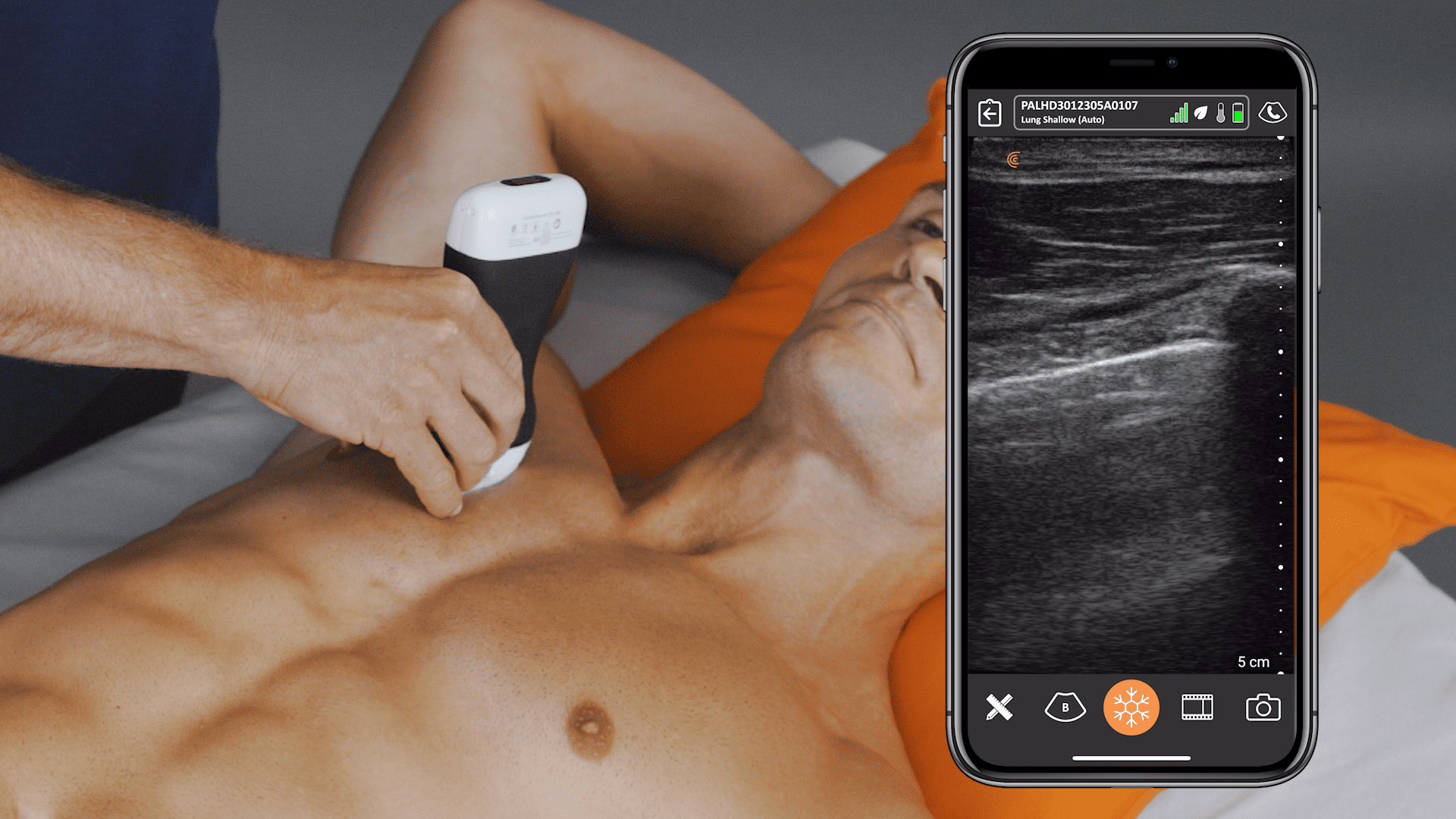
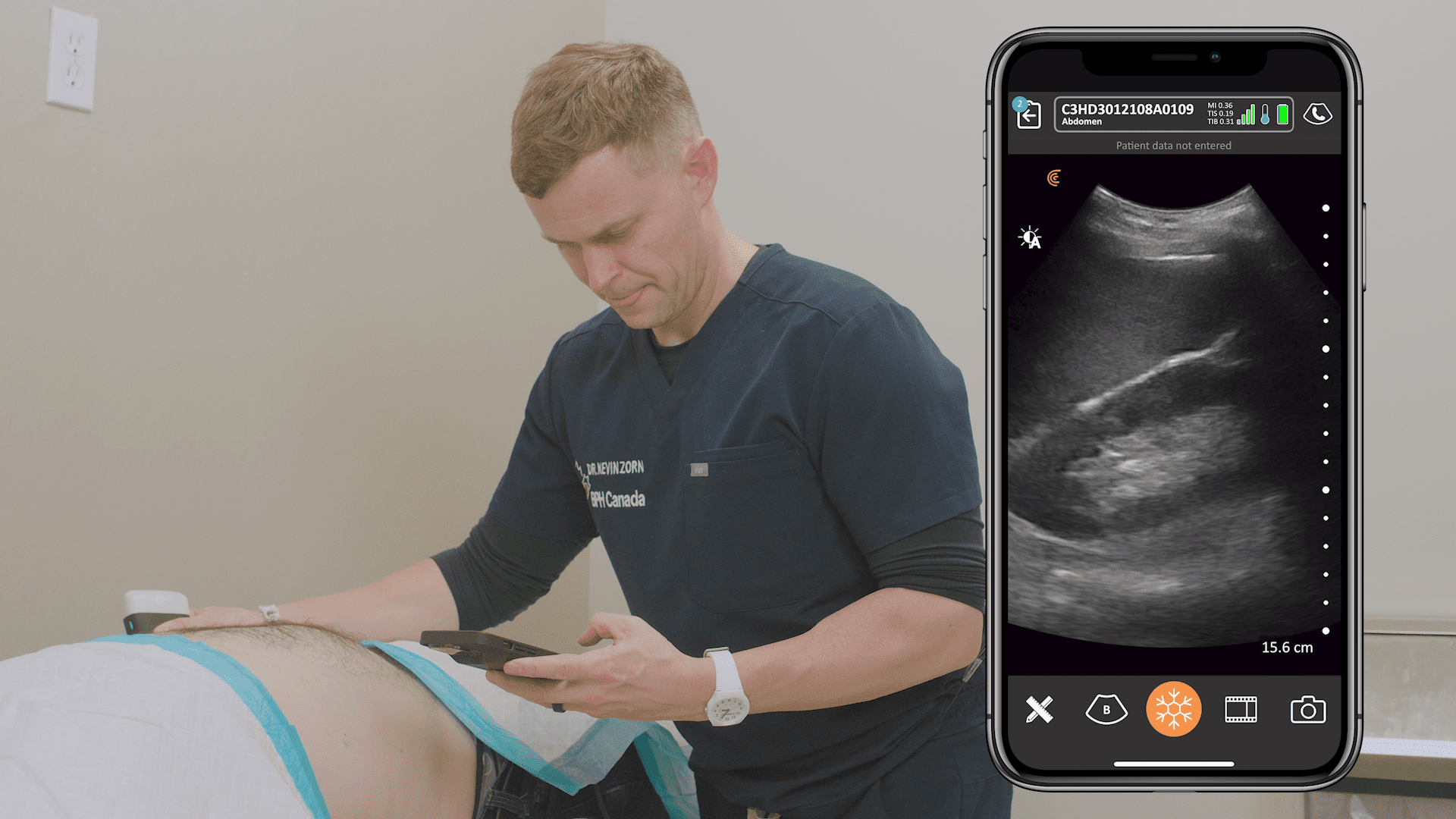
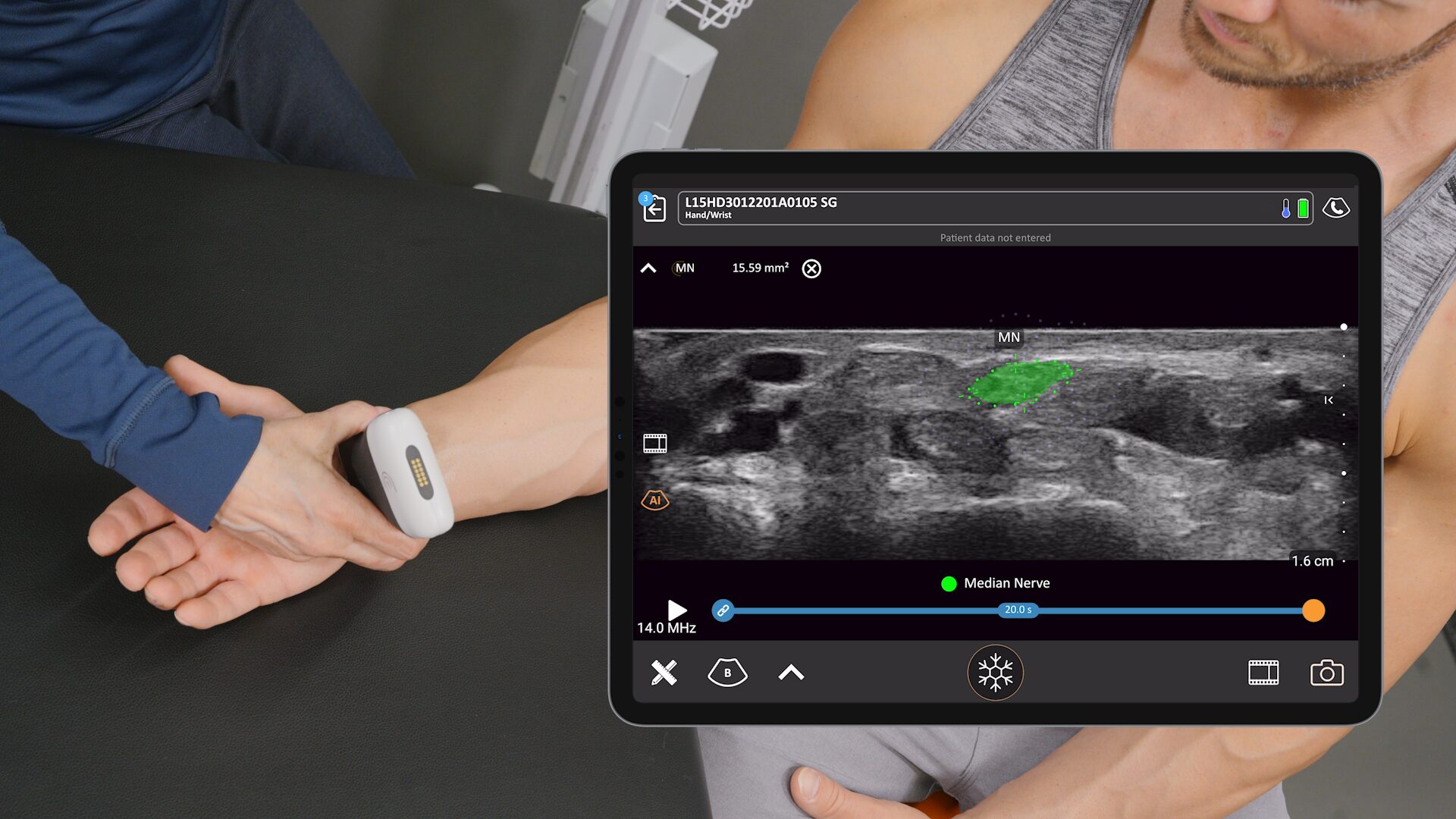
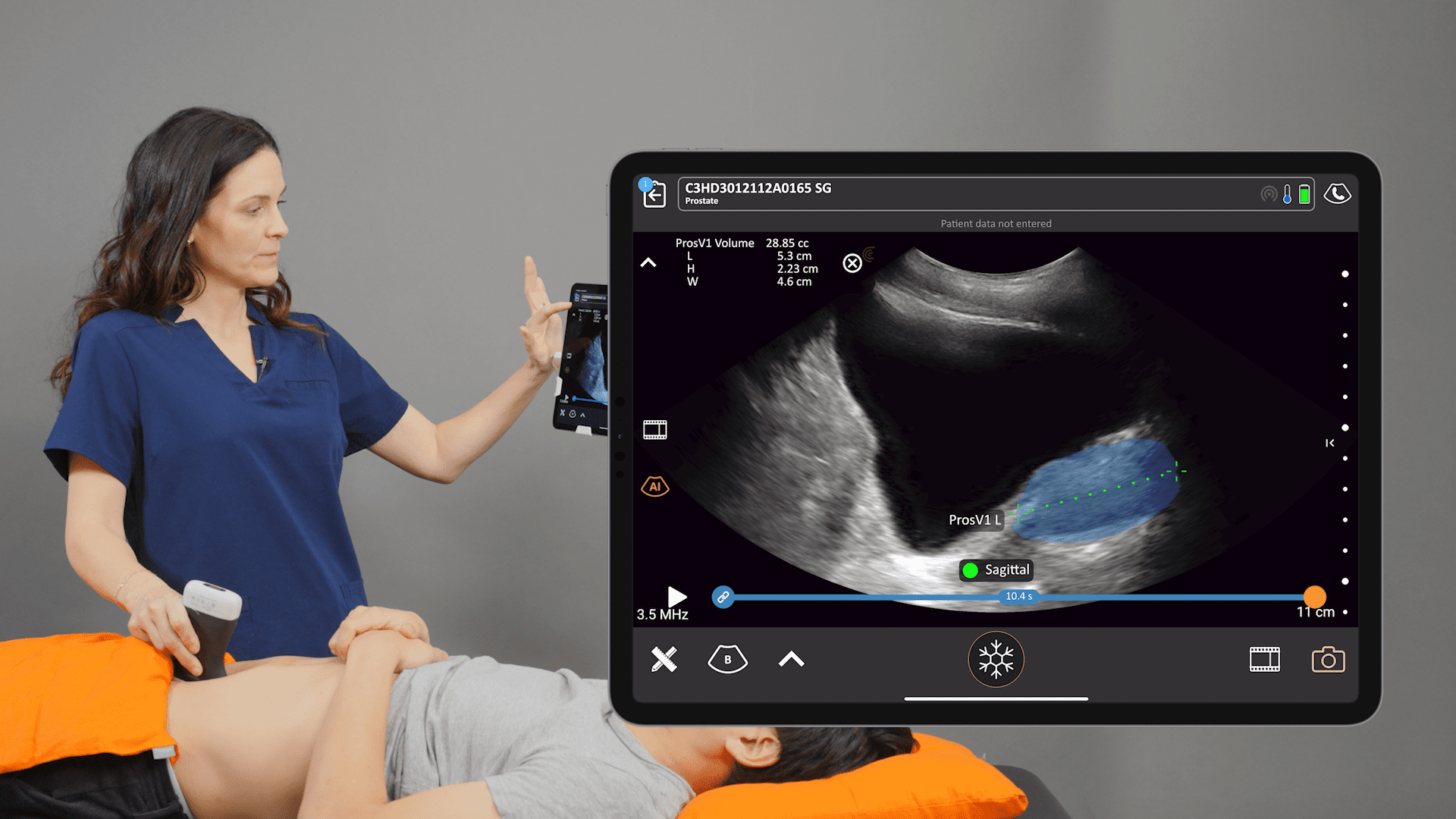
Pocket-sized and without wires to keep clean, Clarius ultrasound speeds disinfection and enables physicians to quickly triage and monitor patients. The Clarius PA HD3 delivers the high-definition imaging and performance of traditional ultrasound systems in a highly affordable ultra-mobile scanner that pairs with most iOS and Android devices. Offering more flexibility for whole body imaging, the Clarius PAL HD3 combines the imaging power of the low-frequency phased array for deep cardiac, lung, and abdominal imaging to 40 cm with the high-frequency linear for superior superficial imaging.
Learn more about Clarius for emergency medicine and primary care. Contact us for a personal virtual demo if you’d like to discuss which Clarius scanner is right for your practice.